Guide to the Norsemen- a highlight of Scandinavian History
What is it that we know of this 2500 years old era?
Sure, the first words to associate with these Norsemen warriors are somewhere between invaders, barbarians, and ruthless fighters. But, there is so much more to these men, their history so rich that we may not have enough papers to define their legacy.
Hence, let’s move on to understanding a little about everything related to Vikings:
Who they were, where did they come from, their culture, their customs and their practices.
Let us now sail back to 800 A.D and study the birth, growth, and ultimately the sinking of this world-renowned historical age.
Who were the Vikings and their Origin?

The Vikings came from the area we today know as Norway, Sweden, and Denmark, in short, the Scandinavia. They were small groups of people belonging to different religions all coming together, to form a big group with the same goal. The goal was to conquer and expand and break free from the trade imbalances and power struggles.
Initially, lesser of the Norsemen would indulge in trade and raid missions, preferring to work as farmers and fishermen.
The settlements too consisted of small farming localities where power laid in hands of district chieftains and his allies. The families resided in longhouses. The benches around the fire acted as beds for the families to sleep during nights and as seats during days.
The longhouses also had a big area for livestock and a storage area for every kind of edible. The cattle and other food stock were all shared by the families living in the respective longhouses. The most-adored drink for Vikings was the mead- an alcoholic beer with honey.
The start of the Viking Era:
Viking Ships
The Viking Ship technology is well-reputed even today. The highly advance navigation systems are what became the root of the Vikings conquering and expanding their rules. The ships are what made Viking raids so powerful.
The long and huge dragon ships could accommodate around 200 men and survive the roughest of the sea conditions. They also made long journeys possible, reasons how the community grew the way it did.
The Start of Raids
As far as Viking raids go, Lindisfarne raid tops the ferocity, marking the beginning to the growth of the Vikings. The attacking and conquering of Lindisfarne, a wealthy yet unsecured island marked the beginning of the Viking era.
This raid was followed by attacks on Skye, Iona, and Rathlin, taking the European religious monasteries by a storm. The first raid in Europe dates back to 799 where the Vikings attacked St. Philibert’s Island.
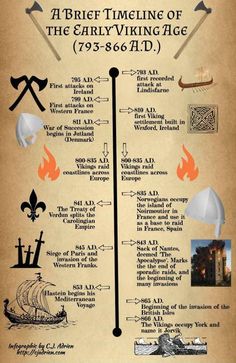
Expanding into British Isles and Europe
Many decades passed with the Vikings attempting minor raids in British Isles, during which they made Frankia (present France and Germany) their allies too. Mid-ninth century was when Scottish, English and Irish land became focus of Vikings.
They first took control of Scottish lands, the next wave to England occurring after 851. Kingdom of Wessex was the only resistance Vikings faced, King Alfred of Wessex becoming the only king in defeating the Danish army.
The fallen Danes set up their homes in North, in the land called “Danelaw” and practiced farming and trading. It was in 952 when the last Scandinavian kind Erik was killed that England got united as one kingdom.
The Vikings faced immense success with the rest of the European land though. Leif Eriksson, the son of Erik, had also been the first European to discover North America after expanding Viking rule to newer heights, capturing Northern France, Iceland and Greenland.
Viking Religion
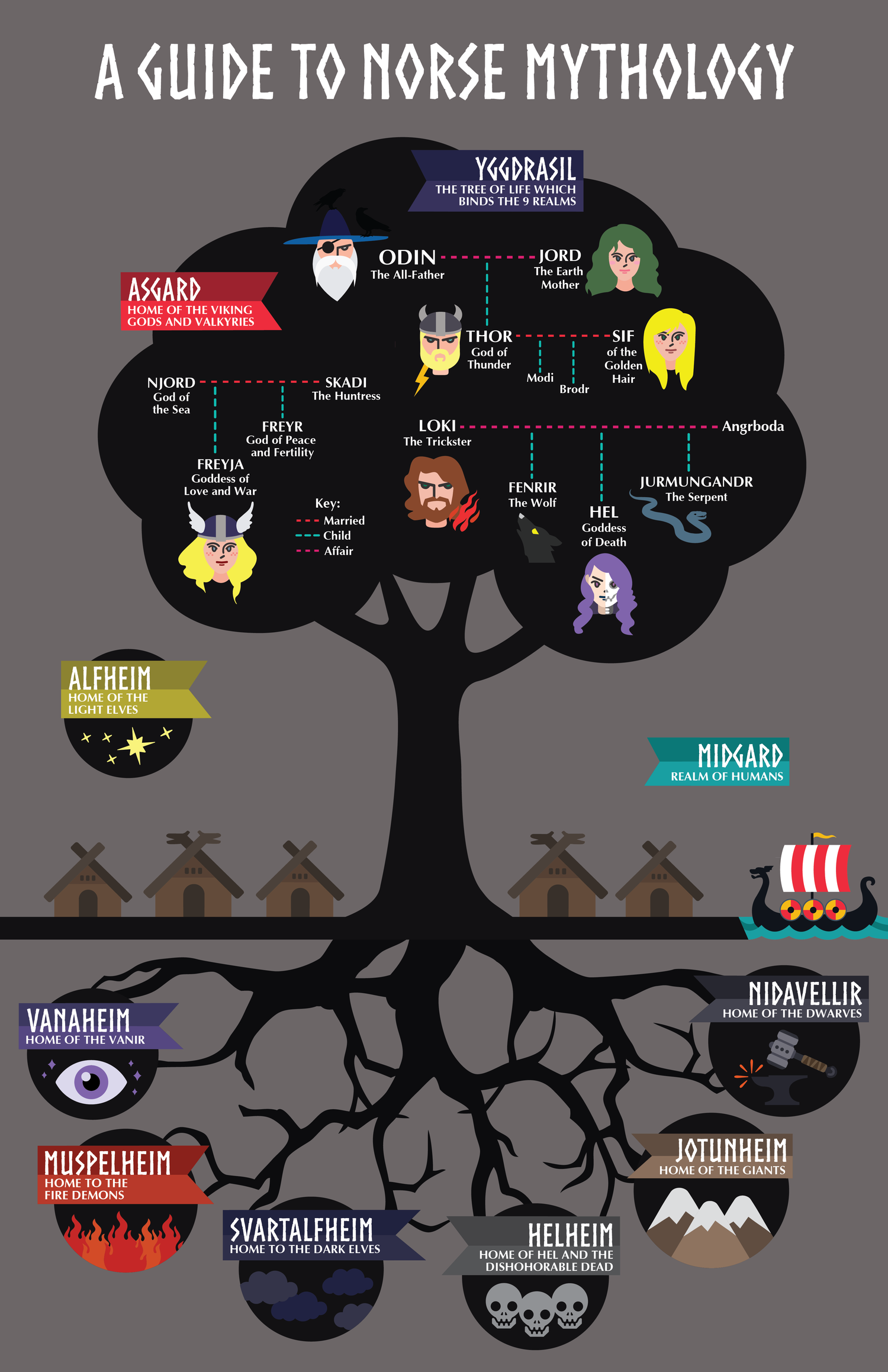
The Vikings followed polytheism, believing in numerous gods and goddesses. They followed numerous rituals, with the kings and chieftains playing significant roles during the sacrifices. Some of the most noteworthy gods included Odin, Thor, and Tyr. Odin was the god is magic, death, and wisdom, Thor as the god of lighting and thunder and Tyr and the god of war.
Viking Fashion and Culture
Viking fashion was also based on the socio-economic classes where the better your rank, the more luxurious clothes you could afford and wear. Although Vikings aren’t people one may associate with fashionable, but fine and high-quality garments were a sign of wealth and upper class. Plus, some Vikings also indulged in rich clothing to attract the opposite gender too.
For Viking women, red was the symbol of esteem and status. Rich women also wore gold or bronze brooches. And, it was the most elite ones who wore silk dresses imported from other areas. For men, they would wear tunics with their overcoats made of thick and long garments alongside leather pants.
The Viking Society
Vikings were intensely male-dominating but women had their own powers too based on their socio-economic ranks.
Men performed trading, raiding, farming and fishing- acting as the providers of their families. Women were the decision makers for domestic issues like cooking, caring for family, cleaning etc. They also had to milk livestock, prepare butter and cheese and preserve food for coming seasons.
Women had the power to divorce their husbands, own lands and even participate in trading. Also, harming women was considered as a shameful act by the community.
As for Viking children, boys were taught by their male family members about ‘men works’. While girls worked with their mothers to garden, cook, make clothes and care for livestock.
Viking’s socio-economic system had 3 categories: Thralls, Karls, and Jarls, with Thralls being the lowest ranking ones- the slaves. Karls- the free men- owned land and livestock and did even engage in works like farming, building longhouses, etc. Jarls were the top tier group, aristocrats owning longhouses, horses and being in charge of political and administrative work. They would also indulge in luxurious sports, hunts and travels.

How the mighty fell apart: the Decline of the Vikings
Viking Age came to a sure and slow decline. In 900s, Christianity began to spread more and more in Norway, causing alterations in the power structure. It was in 1066, that situations of England led to an official end of the Viking Era.
All the Viking culture began to transform into Christian Europe. Today, rare hints of Vikings remain only in the Scandinavia in form of place names, vocabulary etc. It is in Iceland though, that Vikings left their huge impact in literature and sagas about their famed legacy.

